Overview
Scarlet fever is a contagious infection that mostly affects young children. It's easily treated with antibiotics.
Check if you have scarlet fever
The first signs of scarlet fever can be flu-like symptoms, including a high temperature a sore throat and swollen neck glands (large lump on the side of your neck).
A rash appears 12 to 48 hours later. It looks like small raised bumps and starts on the chest and tummy, then spreads. The rash makes your skin feel rough, like sandpaper.
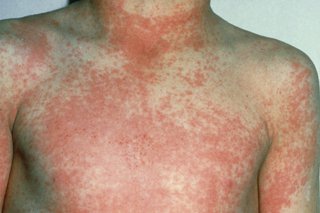
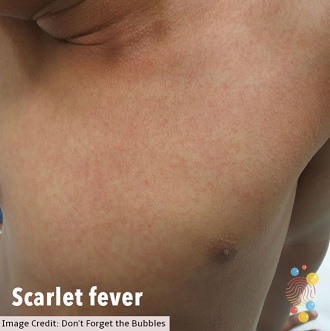
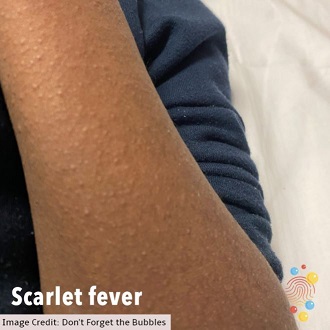
On white skin the rash looks pink or red. On brown and black skin it might be harder to see a change in colour, but you can still feel the rash and see the raised bumps.
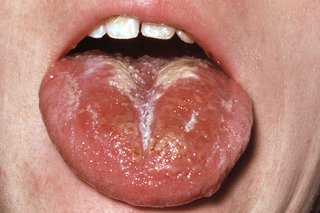
A white coating also appears on the tongue. This peels, leaving the tongue red, swollen and covered in little bumps called ("strawberry tongue").
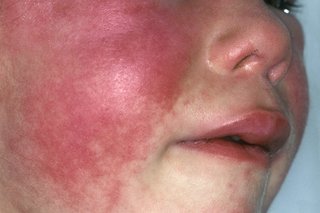
The rash does not appear on the face, but the cheeks can look red. The redness may be harder to see on brown and black skin
The symptoms are the same for children and adults, although scarlet fever is less common in adults.
See a GP if you or your child:
- have scarlet fever symptoms
- do not get better in a week (after seeing a GP)
- are ill again weeks after scarlet fever got better - this can be a sign of a complication, such as rheumatic fever
- are feeling unwell and have been in contact with someone who has scarlet fever
Scarlet fever is very easily spread. Check with a GP before you go in. They may suggest a phone consultation.
What happens at your appointment
GPs can often diagnose scarlet fever by looking at your tongue and rash.
Sometimes they may:
- wipe a cotton bud around the back of the throat to test for bacteria
- arrange a blood test
Treating scarlet fever
Your GP will prescribe antibiotics. These will:
- help you get better quicker
- reduce the chance of a serious illnesses, such as pneumonia
- make it less likely that you'll pass the infection on to someone else
Taking antibiotics
Keep taking the antibiotics until they're finished, even if you feel better.
Things you can do yourself
You can relieve symptoms of scarlet fever by:
- drinking cool fluids
- eating soft foods if you have a sore throat
- taking painkillers like paracetamol to bring down a temperature (do not give aspirin to children under 16)
- using calamine lotion or antihistamine tablets to ease itching
How long scarlet fever lasts
Scarlet fever lasts for around 1 week.
You can spread scarlet fever to other people until 24 hours after you take your 1st dose of antiobotics.
If you do not take antibiotics,you can spread the infection for 2 to 3 weeks after your symptoms start.
Important - If you or your child has scarlet fever, stay away from nursery, school or work for 24 hours after taking the first dose of antibiotics.
Is scarlet fever dangerous?
Scarlet fever can be a serious illness, but thanks to antibiotics it's less common than it used to be and easier to treat.
But cases of scarlet fever have increased in recent years. For more information see GOV.UK: Scarlet fever guidance and data.
Complications are rare but can include:
Pregnancy advice
There's no evidence to suggest that getting scarlet fever during pregnancy will harm your baby.
But it can make you feel unwell, so it's best to avoid close contact with anyone who has it.
Contact a GP if you get symptoms.
Many of the antibiotics used for scarlet fever are considered to be safe to take during pregnancy.
How to avoid spreading scarlet fever
Scarlet fever is very infectious and can easily spread to other people.
To reduce the risk of spreading scarlet fever:
Do:
- wash your hands often with soap and warm water
- use tissues to trap germs from coughs or sneezes
- bin used tissues as quickly as possible
Don't:
- do not share cutlery, cups, towels, clothes, bedding or baths with anyone who has symptoms of scarlet fever